Human-machine interaction plays a central role in numerous applications – from assistive technologies such as exoskeletons, orthoses, and prostheses to industrial assistance systems and robotics. Significant challenges arise when machines work directly with humans, whether in mobility support, rehabilitation, the control of robotic arms, or enhancing physical performance. Successful and safe interaction requires precise monitoring of human behavior, reliable sensor systems, user-friendly interfaces, and intuitive interaction strategies.
The Department of Measurement and Sensor Technology (MUST) leverages its extensive expertise in hardware design and its interdisciplinary collaboration within the graduate research group LokoAssist (GRK 2761, Project No. 450821862). Only through cooperation with research groups from various disciplines can the interdisciplinary challenges
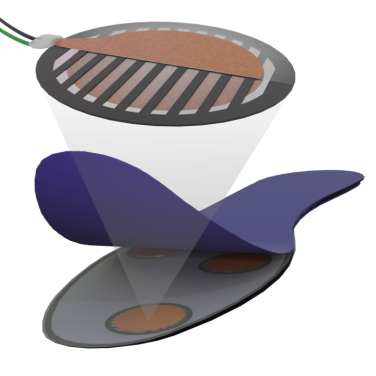
Sensor-integrated Insole
Our 3D-printed insoles with ferroelectret sensors revolutionize gait detection for wearable robotics. Lightweight, cost-effective, and precise, they track key gait events, such as heel strikes, with minimal delay, enabling seamless biomechanics analysis and exoskeleton control. Designed to support natural movement without laboratory constraints, they pave the way for new advancements in rehabilitation and assistive robotics. Further details can be found in the publication.
Vibrotactile Feedback
Vibrotactile signals can be a helpful addition to visual information. Using multiple vibration motors in an appropriate arrangement, enables to convey more complex information, e.g. direction. In the context of human-robot interaction, such an interface constitutes an information channel that can be used by the robot to communicate with the human.
The illustrated wearable interface uses a vibrotactile illusion to generate vibrotactile cues across all circumferential locations around the human arm. Further details can be found in the publication.
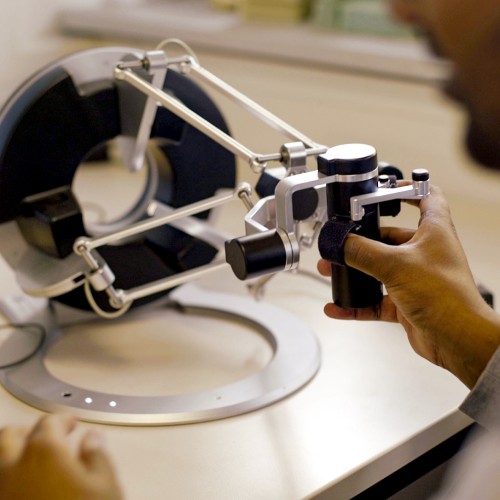

3D Input with Haptic Feedback to the User
The omega.7 from force dimension can be used like a 3D mouse with additionally programmable haptic feedback to the user. For instance, we can map complex impedance behavior to the handle.
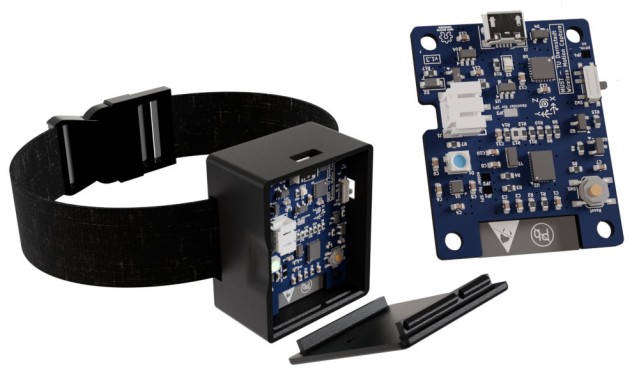
Wireless Inertial Motion Capture System
Inertial motion capture provides valuable data in fields like biomechanics, robotics, and human-computer interaction by portable and efficient movement tracking. Our wearable motion capture system integrates open-source hardware with a modular software framework, which offers compatibility with the biomechanical tools OpenSim and OpenSense. The system features automatic sensor-to-segment alignment for self-calibration using arbitrary motion data, promoting plug-and-play functionality. Further technical details and results can be found in the corresponding publication.
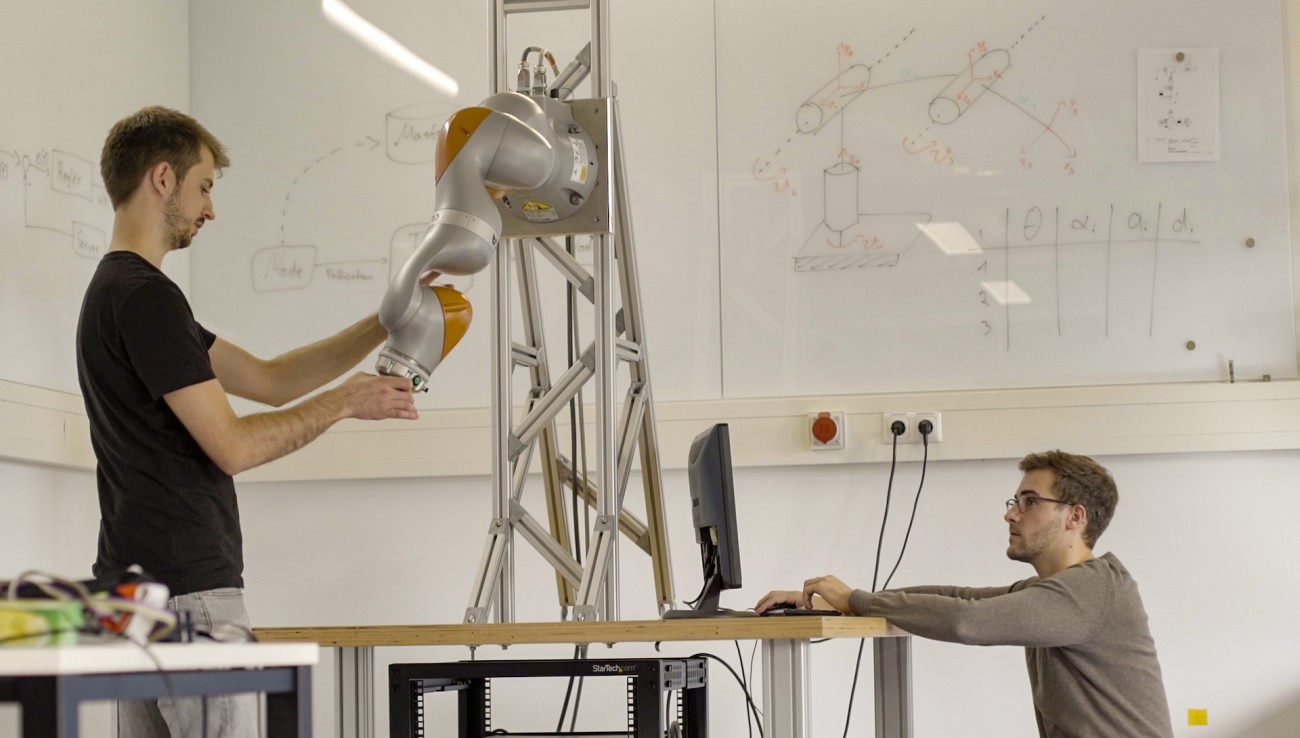
Robot Out of the Printer
In his Bachelor's thesis, Felix Herbst designed this easy to manufacture prototype of a 3D printed 6-axis robot. It is now in its third generation and has been replicated for use across multiple experiments. More information about the backgrounds in this article (German only) by Mareike Hochschild.
Exoskeleton
Exoskeletons are wearable robotic systems that enhance the power and assist the accuracy of both healthy and disabled individuals. By combining the best of both worlds we can design intelligent human-machine systems for power-assistance, rehabilitation, teleoperation and haptic interaction in virtual reality.
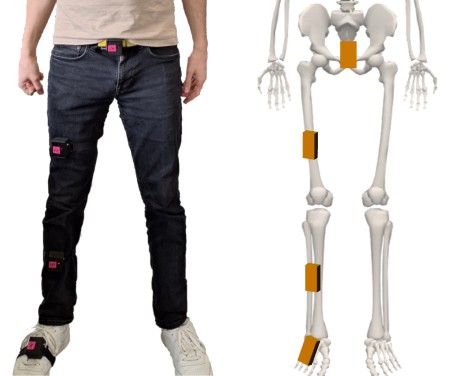
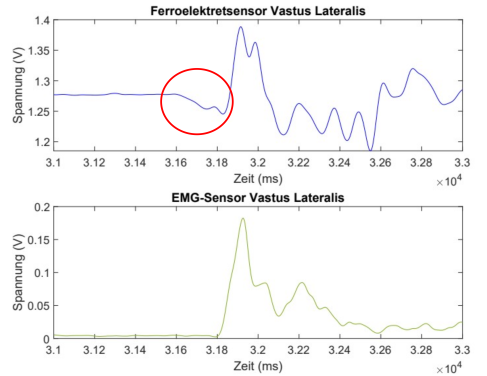
Motion intention detection
For intuitive and seamless human-machine interaction when using exoskeletons or active prostheses, the use of suitable sensor systems is essential for effective mobility assistance. Especially for everyday use, the sensors need to be as unobtrusive as possible. In our research, we are developing our own force sensors based on ferroelectrets to detect the deformation of individual muscles and infer the user's intention. We use these sensors in everyday tasks such as standing up, which is particularly challenging for people with disabilities. With these systems, we want to give people with limited mobility back some quality of life in their everyday lives. Details and results are explained in the publication.
Continuum Robot
In contrast to conventional rigid-link robots, continuum robots feature a continuous backbone which replaces vertebrates. The flexible structure offers new capabilities such as performing full body deformation. Continuous joints also remove the dependency on small discrete joints and therefore enable the possibility of advanced miniaturization. Applications for continuum robots are broad including search and rescue operations, object manipulation, and interventional medicine.
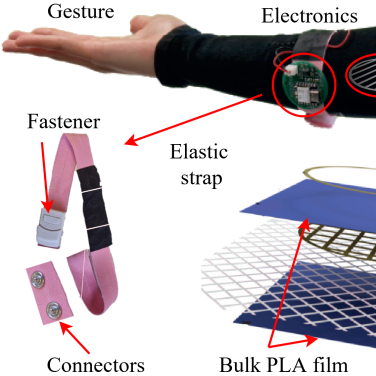
Gesture Detection
The recognition of hand gestures enables intuitive control of exoskeletons, wearable devices, and interactive systems. Our research focuses on the use of highly sensitive ferroelectret sensors made from biocompatible materials such as PLA. These sensors precisely capture movements and can be seamlessly integrated into textiles like sports bandages. A clip-on electronics module processes the signals.
The sensors can detect gestures such as an open or closed fist, as well as variations in their execution. In the future, these technologies could be used not only for gesture recognition but also for actuation, for instance, in exoskeletons. They create a comfortable and versatile interface between humans and machines.
For more information, see the related publication (gesture detection) und publication (textile-based sensor).
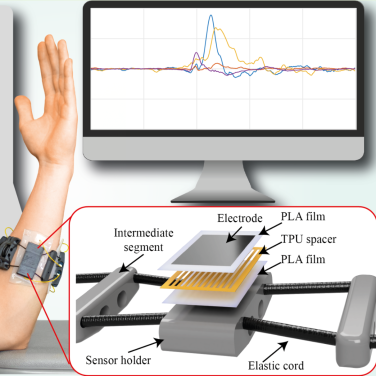
Biocompatible ferroelectret sensor made from PLA for sensitive detection and differentiation of multiple gestures.