Paper accepted: Harnessing Spatial Diversity for Physical Layer Security without Adversary Channel Knowledge
New IEEE TWC publication introduces BeamSec, a beam hopping method that improves secrecy in mmWave communication systems without knowing eavesdroppers’ channels.
2025/07/29
BeamSec combines beam hopping with adaptive time allocation to maximize secrecy in mmWave systems, even when there is no knowledge about the location or channel of eavesdroppers. Experiments with a 60 GHz testbed show that BeamSec achieves a non-zero secrecy rate and significantly improves security without requiring additional hardware.
Millimeter-wave (mmWave) communication systems utilize phased-array antennas to generate highly directional beams, effectively reducing the signal footprint. Nonetheless, eavesdropping, particularly within the main-lobe, remains a significant concern.
This paper introduces BeamSec, a novel beam hopping approach to maximize absolute secrecy rates with no information about the channel state information (CSI) or location of the eavesdroppers. Methodologically, BeamSec identifies diverse beam-pairs between transceivers by analyzing signal characteristics, such as Angle of Departure (AoD) and Angle of Arrival (AoA). To prevent the secure message from being eavesdropped, BeamSec splits and jointly encodes data among selected beams.
Moreover, BeamSec optimizes secrecy by adapting time allocation across selected beams under different levels of channel knowledge, namely (i) full/partial Radio Frequency (RF) maps constructed based on the empirical data of legitimate users, (ii) knowledge of the room floor map, and (iii) only the instantaneous knowledge of the legitimate transmitter (TX)-receiver (RX) channel.
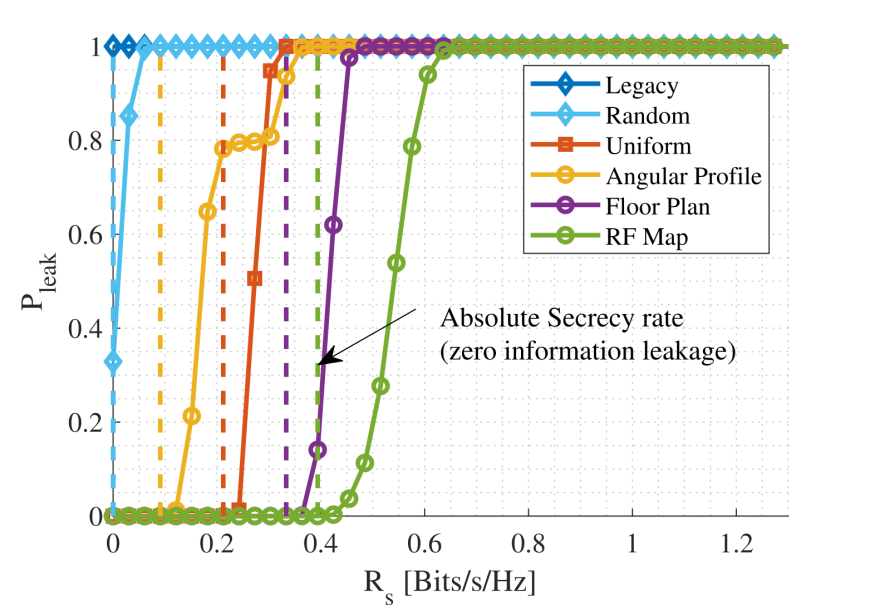
Furthermore, we experimentally validate the efficiency of the proposed schemes using an 802.11ad-compatible 60 GHz phased-array testbed. Specifically, BeamSec demonstrates a non-zero absolute secrecy rate even for the simplistic uniform time allocation approach. Radio map (partial channel knowledge) and known room geometry (instantaneous TX/RX) based schemes provide further improvement of 124.8% and 58.13%, respectively, as compared to uniform time allocation.
Authors: Afifa Ishtiaq, Ladan Khaloopour, Vahid Jamali, Matthias Hollick, Arash Asadi
Published in: IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 26 July 2025

